- Employers must demonstrate a genuine redundancy situation, such as a workplace closure or a reduced need for specific types of work, to avoid unfair dismissal claims.
- Meaningful consultation is mandatory for all redundancies, with collective consultation required if 20 or more employees are affected within a 90-day period.
- Selection criteria must be objective and non-discriminatory to prevent claims under the Equality Act 2010.
- Statutory redundancy pay is a legal right for employees with at least two years of continuous service, calculated based on age, length of service, and weekly pay.
- Settlement agreements are only legally binding if the employee receives independent legal advice from a qualified solicitor or certified trade union official.
Checklist for a Legally Compliant Redundancy Process
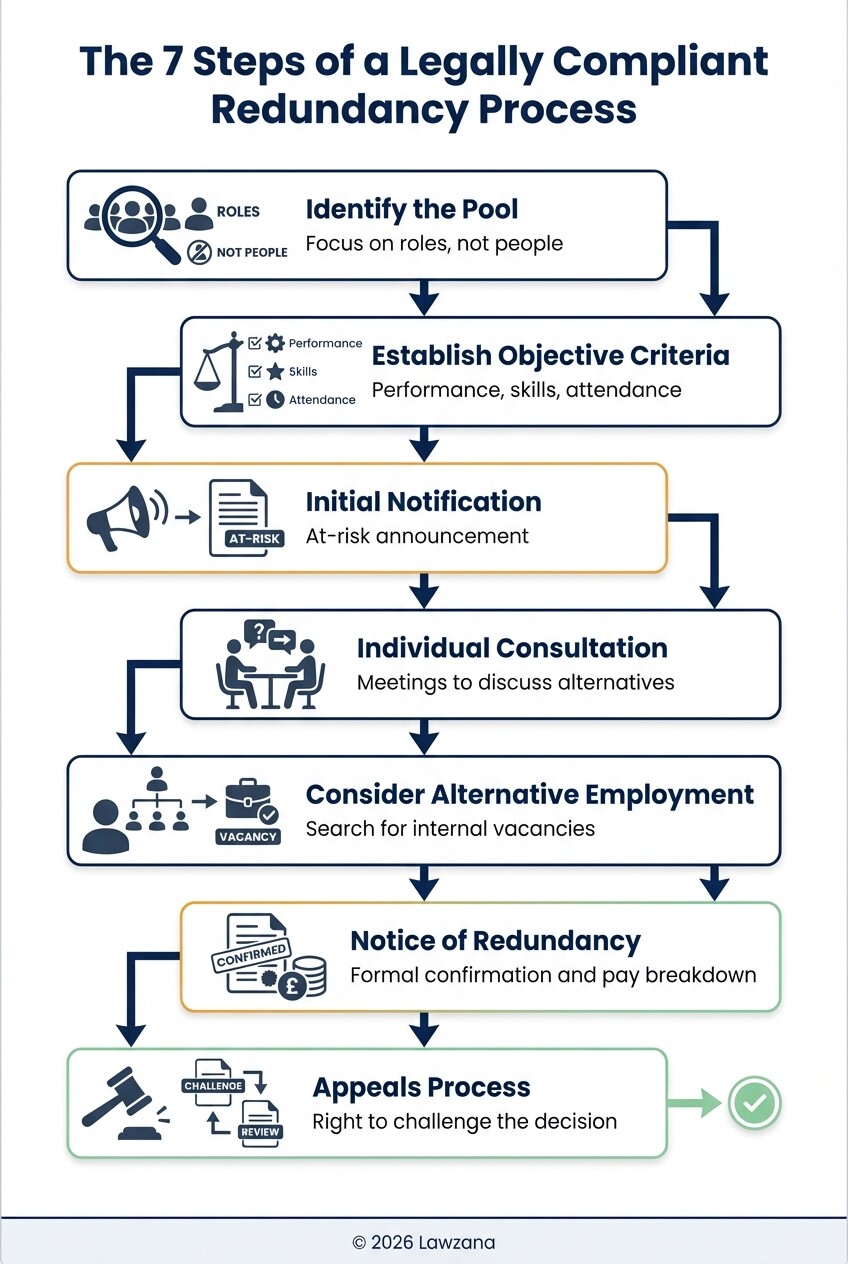
A fair redundancy process in the UK follows a strict chronological order to protect the business from litigation. Failure to follow these steps often leads to "procedural unfairness," even if the reason for the redundancy itself is valid.
- Identify the Pool: Determine which roles are at risk. Avoid targeting individuals; focus on the functions that are no longer required.
- Establish Objective Criteria: Use measurable factors such as performance records, skills/qualifications, and disciplinary records. Avoid "last in, first out" if it disproportionately affects younger or older employees.
- Initial Notification: Inform the affected pool that they are at risk of redundancy and explain the business rationale.
- Individual Consultation: Hold at least two to three meetings with each employee to discuss the selection criteria, alternative roles, and ways to avoid redundancy.
- Consider Alternative Employment: You are legally required to search for and offer suitable alternative vacancies within the organization or group.
- Notice of Redundancy: Issue a formal letter confirming the redundancy, the notice period, and the final payment breakdown.
- Appeals Process: Provide a mechanism for the employee to appeal the decision, typically handled by a manager not involved in the initial selection.
Sample Settlement Agreement Clause (Full and Final Settlement)
When resolving an employment dispute, a "Full and Final Settlement" clause is the most critical element of the documentation. This language ensures the employee cannot pursue further claims in an Employment Tribunal.
"The Employee accepts that the terms of this Agreement are in full and final settlement of all and any claims, whether statutory, contractual, or otherwise, which the Employee has or may have against the Employer or any Group Company arising out of or in connection with their employment or its termination. This includes, but is not limited to, claims for unfair dismissal, breach of contract, and discrimination under the Equality Act 2010."
Fair Selection Criteria and Consultation Processes
Fair redundancy selection requires a balance of transparency and data-backed decision-making. Employers must move away from subjective "manager's choice" models and toward scoring matrices that can be defended in court.
Selection criteria must be applied consistently across the entire "pool" of affected employees. Common fair criteria include attendance records (excluding pregnancy-related or disability-related absences), documented performance reviews, and specialized technical skills. Avoid criteria that could be perceived as "indirect discrimination," such as selecting part-time workers first, as this often disproportionately affects women.
Consultation is not just a formality; it is a legal requirement to listen to employee counter-proposals. For individual redundancies, the law does not specify a minimum duration, but it must be "meaningful." For collective redundancies (20+ people), consultation must start at least 30 days before the first dismissal, increasing to 45 days if 100 or more people are affected.
Calculating Statutory Redundancy Pay in 2026
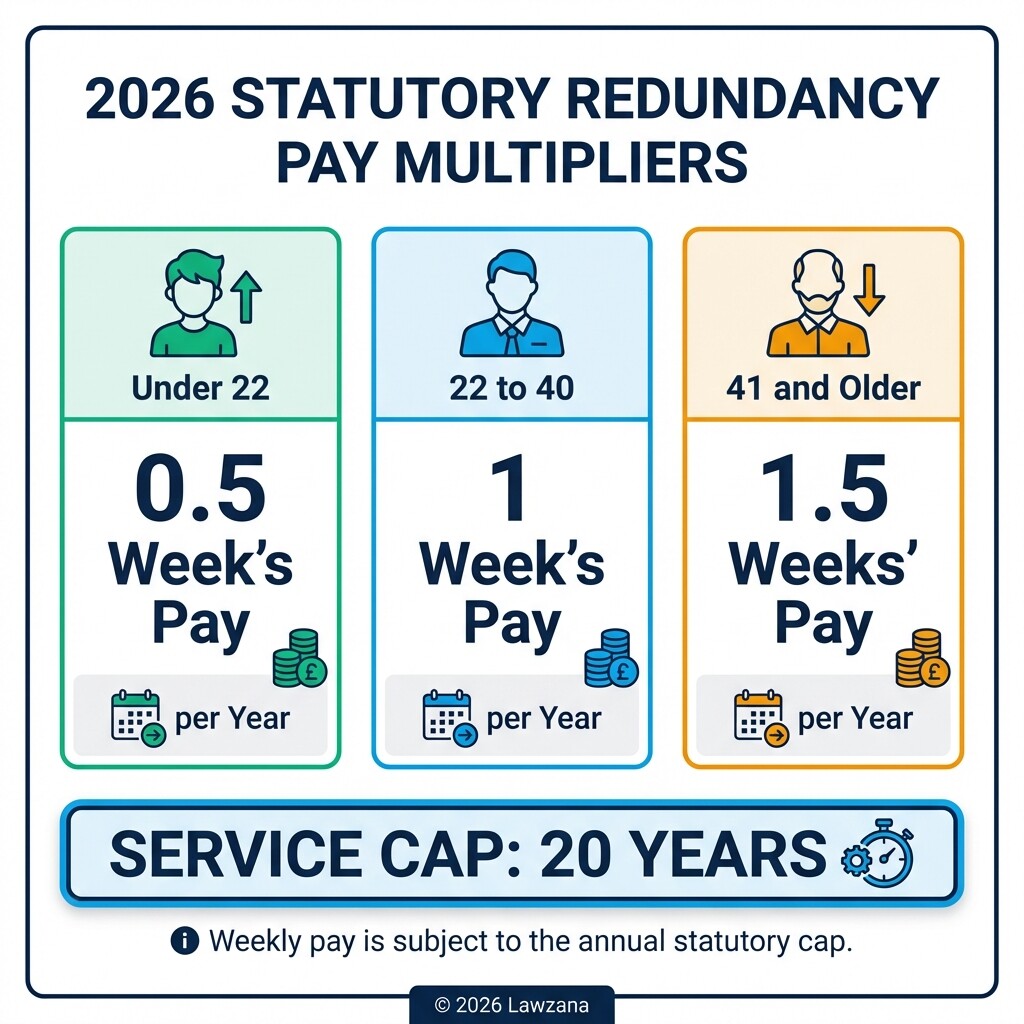
Statutory redundancy pay is the minimum amount an employer must pay an eligible employee by law. As of 2026, these rates are adjusted annually to reflect inflation and changes in the national average wage.
To qualify, an employee must have at least two years of continuous service. The calculation is based on the following three-tier age system:
| Age Range | Payment Calculation |
|---|---|
| Under 22 | 0.5 week's pay for each full year of service |
| 22 to 40 | 1 week's pay for each full year of service |
| 41 and older | 1.5 weeks' pay for each full year of service |
The total length of service is capped at 20 years. Weekly pay is also subject to a statutory cap, which is updated every April by the UK government. Employers must provide a written statement showing how the redundancy payment was calculated. Failure to pay the correct amount can lead to a breach of contract claim in a civil court or an Employment Tribunal.
Avoiding Unfair Dismissal and Discrimination Claims
Unfair dismissal claims are the most common legal challenge following a redundancy exercise. To defend against these, an employer must prove that redundancy was the "real" reason for dismissal and that they acted reasonably in the circumstances.
Discrimination claims are even more dangerous for businesses because, unlike unfair dismissal, there is no cap on the compensation an Employment Tribunal can award. If an employee can show that their selection was influenced by a "protected characteristic"-such as age, disability, race, or sex-the business faces significant financial and reputational risk.
To mitigate these risks:
- Document Everything: Keep detailed notes of all consultation meetings and the specific reasons for every score in the selection matrix.
- Trial Periods: Offer a four-week trial period for any alternative roles to prove the business made a good-faith effort to retain the employee.
- Fair Notice: Ensure the employee is given their full contractual or statutory notice period, whichever is longer.
Documentation Required for Settlement Agreements
A settlement agreement is a legally binding contract that waives an employee's right to sue in exchange for a financial sum. For these to be valid under UK law, specific conditions must be met regarding the documentation and the advice provided.
The agreement must be in writing and relate to a particular "complaint" or "proceedings." It must identify a "relevant independent adviser" who has provided legal advice to the employee. This advisor must be covered by professional indemnity insurance. Without these elements, the agreement is void, and the employee can still bring a claim against the company despite having received the settlement money.
Standard documentation for a settlement package should include:
- The effective date of termination.
- A breakdown of the settlement payment (ex-gratia) vs. contractual payments (notice and holiday pay).
- Tax indemnities (confirming the employee is responsible for tax above the £30,000 exemption).
- Confidentiality and non-derogatory comment clauses.
- A letter of reference template.
Recent Shifts in Employment Tribunal Procedures
The UK Employment Tribunal system has moved toward a "Digital-First" model in 2026 to clear the backlog of cases. This shift impacts how businesses must prepare for potential litigation following a redundancy dispute.
Evidence must now be uploaded to a centralized digital portal, and "Video Hearings by Default" are standard for preliminary and short-form hearings. This requires businesses to maintain impeccable digital records of the redundancy process. Furthermore, the ACAS (Advisory, Conciliation and Arbitration Service) Early Conciliation process remains a mandatory first step, but 2026 regulations have tightened the timelines for reaching a settlement before a formal claim is lodged.
Tribunals are also increasingly using "Witness Statement Directions" that limit the length of written evidence. This means businesses must be concise and focused on the procedural fairness of their redundancy strategy rather than relying on voluminous, irrelevant documentation.
Common Misconceptions About UK Redundancy
Myth 1: "Last In, First Out" (LIFO) is the safest selection method. LIFO is no longer considered the gold standard and can actually be illegal. It often discriminates against younger employees who have shorter service histories, potentially leading to age discrimination claims. Objective skills-based scoring is much safer.
Myth 2: You can make a person redundant because they are an underperformer. Redundancy is about the role, not the person. If you use a redundancy process to remove a "problem" employee while the role itself still exists, this is a "sham redundancy." The employee will likely win an unfair dismissal claim. Performance can be a factor in selection criteria, but it cannot be the sole reason for the redundancy.
Myth 3: Small businesses don't have to follow the same consultation rules. While collective consultation (20+ people) has specific statutory timelines, the requirement for a "fair process" and "individual consultation" applies to every UK employer, regardless of size. Even a business with one employee must follow a fair procedure to avoid litigation.
FAQ
How much is the statutory redundancy pay cap in 2026?
The cap is adjusted every April based on the Retail Prices Index (RPI). For the 2025/2026 tax year, employers should consult the latest figures on GOV.UK to ensure they are using the updated weekly maximum.
Can an employee be made redundant while on maternity leave?
Yes, but they have enhanced protections. If their role is made redundant, they must be offered any suitable alternative vacancy as a priority over other employees. Failure to do so is automatically unfair dismissal.
What happens if I don't follow the consultation period?
If you fail to comply with collective consultation requirements, an Employment Tribunal can award a "Protective Award." This is a penalty of up to 90 days' gross pay per employee, which can be financially devastating for a business.
Is redundancy pay taxable in the UK?
The first £30,000 of a redundancy payment (the "ex-gratia" or compensation element) is usually tax-free. However, contractual payments like notice pay (Payment in Lieu of Notice) and accrued holiday pay are subject to standard Income Tax and National Insurance contributions.
When to Hire a Lawyer
You should consult a solicitor specializing in UK employment law if you are planning a redundancy that affects more than 20 people, or if you are dealing with a high-level executive dismissal. Legal expertise is also essential if an employee raises a formal grievance during the consultation period or if you are served with an ET1 claim form from the Employment Tribunal. Engaging a lawyer early can often prevent a dispute from reaching a full hearing through strategic settlement negotiations.
Next Steps
- Review Insurance: Check if your business has Employment Practices Liability Insurance (EPLI) to cover legal costs.
- Draft a Business Case: Document the financial or structural reasons for the redundancies before announcing them.
- Contact ACAS: Familiarize yourself with the current ACAS Code of Practice on disciplinary and grievance procedures, which Tribunals use as a benchmark for fairness.
- Prepare Documentation: Standardize your scoring matrices and consultation invitation letters to ensure consistency.


