- Prioritize Registration: Vietnam is a "First-to-File" jurisdiction, meaning rights are generally awarded to the first person to file an application, regardless of prior use.
- 2026 Digital Shifts: All IP filings are now centralized through the IP Vietnam online portal, requiring digital certificates for foreign entities via local representatives.
- Administrative Enforcement: While courts are evolving, administrative actions through the Market Surveillance Agency remain the fastest way to stop infringements.
- Software Protections: Computer programs are protected as literary works under copyright law, but specific functional aspects may qualify for "Utility Solution" patents.
- Local Representation: Foreign entities without a permanent residence or head office in Vietnam must appoint a licensed local IP agent to interact with the authorities.
Tech IP Protection Checklist for Vietnam 2026
Foreign tech firms must secure their assets before entering the Vietnamese market to prevent "bad faith" registrations and data leaks. Use this checklist to audit your readiness.
| Action Item | Description | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Trademark Search | Conduct a clearance search in the IP Vietnam database for brand names and logos. | Critical |
| First-to-File Registration | File applications for trademarks, patents, and industrial designs immediately. | Critical |
| Copyright Recordal | Record software code and UI/UX designs with the Copyright Office of Vietnam (COV). | High |
| NDA/NCA Execution | Ensure all local employees and JV partners sign robust non-disclosure and non-compete agreements. | High |
| Customs Recordal | Register your IP with the General Department of Vietnam Customs to block counterfeit imports/exports. | Medium |
| Domain Name Scrutiny | Register .vn and .com.vn domains through a VNNIC-accredited registrar. | Medium |
New Patent and Trademark Filing Procedures for 2026
Patent and trademark filings in Vietnam now require a digital-first approach through the Intellectual Property Office of Vietnam (IP Vietnam). Foreign applicants must engage a local industrial property agent to navigate the mandatory electronic filing system and handle communications in Vietnamese.
The 2026 landscape emphasizes the "e-filing" mandate, where all documentation, including Power of Attorney (POA) and technical specifications, must be uploaded with certified digital signatures. For tech firms, the "Utility Solution" (Utility Model) remains a popular alternative to standard patents, as it has a lower threshold for inventiveness and a faster registration window.
- Trademark Timeline: Expect 12 to 18 months from filing to registration, assuming no oppositions.
- Patent Timeline: Invention patents typically take 24 to 42 months, while Utility Solutions take 18 to 24 months.
- Costs: Basic trademark filing fees start at approximately 1,000,000 VND to 2,000,000 VND per class (official fees only), excluding professional legal fees.
Copyright Protections in the Digital and AI Landscape
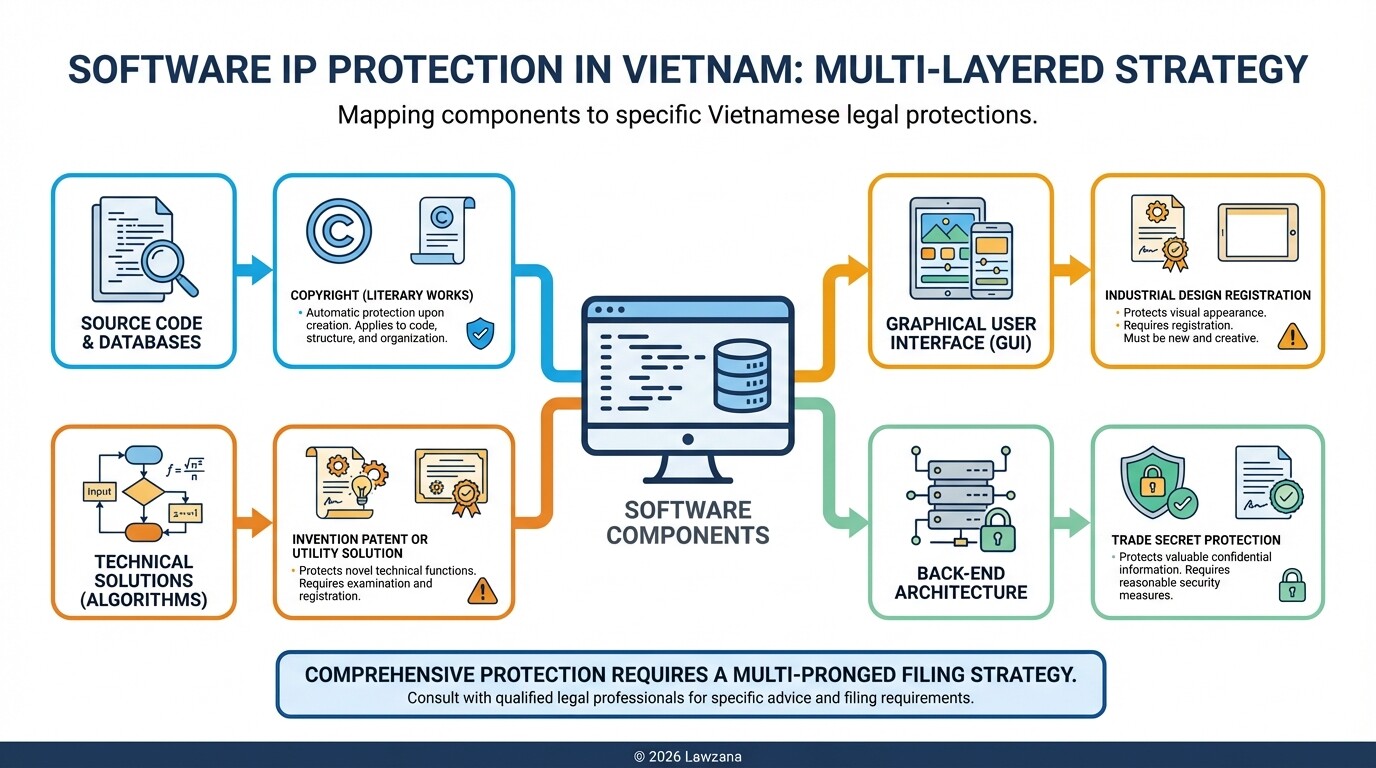
Vietnam's copyright regime protects software, databases, and digital content automatically upon creation, though formal recordal is highly recommended for enforcement. As of 2026, the law clarifies that AI-generated works lack "authorship" unless there is significant human intervention in the creative process.
For software firms, code is protected as a literary work. However, the most effective protection involves registering the graphical user interface (GUI) as an industrial design and the back-end architecture as a trade secret. Vietnam has also strengthened "Intermediary Service Provider" (ISP) liabilities, making it easier to issue take-down notices to local hosting providers for infringing content.
Sample Software Protection Clause for Vietnam
"The Software, including its source code, object code, and UI/UX design, is the exclusive property of [Company Name]. Pursuant to the Intellectual Property Law of Vietnam, the Developer/Partner hereby assigns all economic rights in any modifications or derivative works to [Company Name] immediately upon creation. Any unauthorized reproduction or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited and subject to statutory damages."
Enforcement of IP Rights Through Administrative and Court Systems
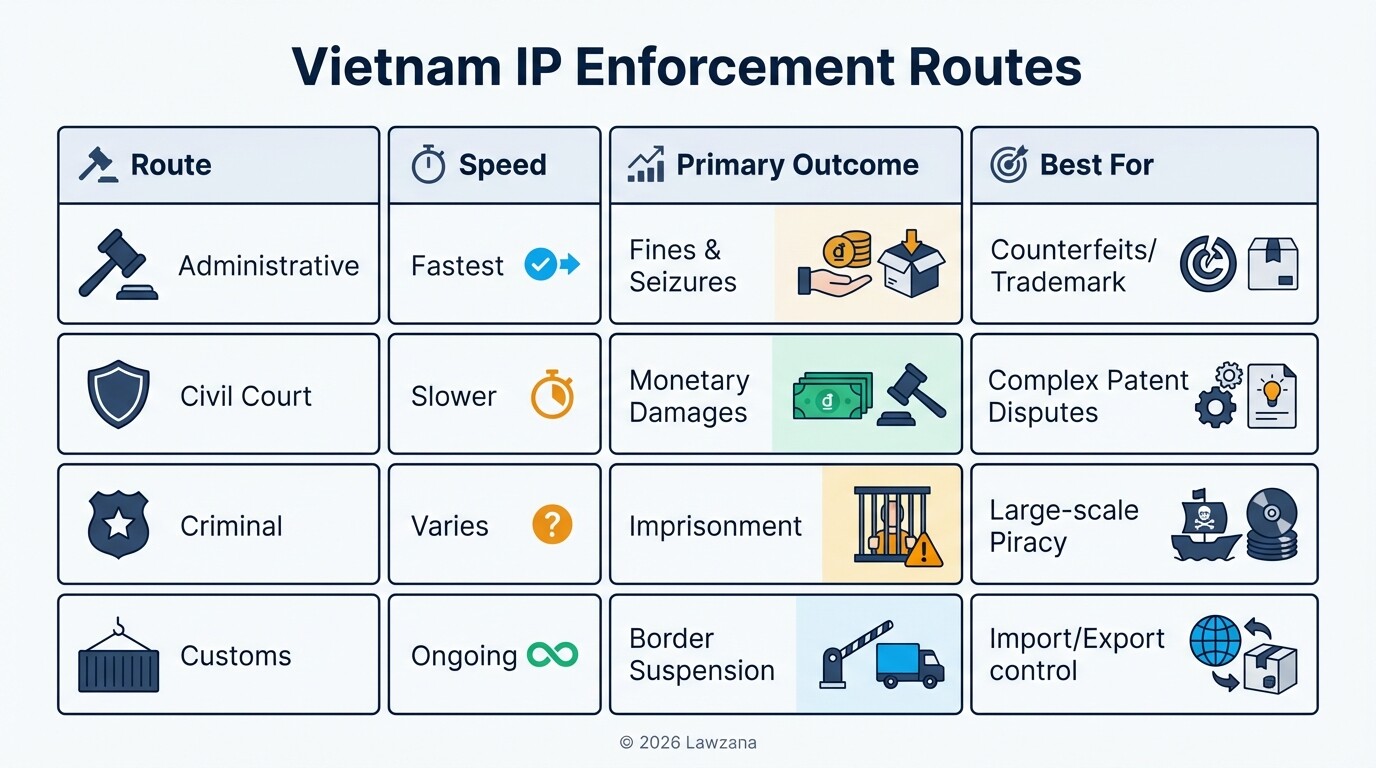
Enforcement in Vietnam is multi-layered, involving administrative authorities, the police, customs, and the civil court system. Most foreign firms prefer administrative actions because they are cost-effective and result in the rapid seizure of infringing goods, even if they do not provide monetary damages to the owner.
- Administrative Action: Agencies like the Inspectorate of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MoST) or the Market Surveillance Agency can issue fines and confiscate goods. This is the primary route for trademark infringement.
- Civil Litigation: Used primarily for complex patent disputes or when seeking significant damages. While the courts are becoming more sophisticated, cases can take 12 to 24 months to resolve.
- Criminal Prosecution: Reserved for large-scale counterfeiting or commercial-scale copyright piracy.
- Customs Procedures: By filing a "Request for Border Control," rights holders can empower customs officials to suspend the clearance of suspected infringing shipments.
Strategies for Managing Trade Secrets in Joint Ventures
Protecting trade secrets in Vietnam requires a combination of strict contractual language and physical security measures, as the law only protects information that is not common knowledge and provides economic advantage. In a Joint Venture (JV), the risk of "leakage" to local partners is high, necessitating a tiered access strategy for sensitive technical data.
Foreign firms should implement the "Principle of Least Privilege" and ensure that all employment contracts include specific Trade Secret provisions. Under Vietnamese law, a trade secret is only legally recognized if the owner has taken "necessary measures" to keep it secret.
Trade Secret Protection Checklist for JVs
- Marking: Clearly label all sensitive documents as "Confidential - [Company Name] Property."
- Access Logs: Maintain digital logs of who accesses source code or hardware schematics.
- Exit Interviews: Conduct formal exit interviews for departing local staff, reminding them of their ongoing confidentiality obligations.
- Security Audits: Perform bi-annual audits of the JV partner's IT infrastructure.
Navigating the First-to-File System as a Foreign Entity
Vietnam's adherence to the "First-to-File" principle means that the person who applies for a trademark or patent first is the legal owner, regardless of who used it first globally. This often leads to "trademark squatting," where local entities register famous foreign brands and then attempt to sell them back to the original owners.
To navigate this, tech firms must file for protection at the earliest possible stage-ideally before even entering negotiations with local distributors or partners. If a squatter has already filed, the foreign entity must prove "bad faith" or rely on "well-known trademark" status, which is a high evidentiary bar in Vietnamese proceedings.
- Proactive Filing: Utilize the Madrid Protocol for international trademark extensions into Vietnam.
- Monitoring: Set up "watch services" to detect new applications that mimic your brand.
- Translation: Register both the English name and the Vietnamese translation/transliteration to prevent others from using a localized version of your brand.
Common Misconceptions
"My US/International Patent automatically covers Vietnam."
Vietnam is a member of the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), but you must still enter the "National Phase" in Vietnam within 31 months of your priority date. There is no such thing as an automatic global patent.
"Software cannot be patented in Vietnam."
While software "as such" is excluded from patentability, "computer-implemented inventions" that solve a technical problem with a technical solution (e.g., a new data encryption method or an optimized hardware-control algorithm) are patentable.
FAQ
How much does it cost to register a trademark in Vietnam in 2026?
Official filing fees start at approximately 1,000,000 VND per class, but total costs including legal representation and translation usually range from $500 to $1,000 USD per application.
Can I protect my tech brand if someone else registered it first?
If the registration was made in "bad faith," you can file a cancellation action. However, this is difficult and expensive. It is much more efficient to file your application before your brand becomes known in the local market.
Is the Madrid Protocol available for Vietnam?
Yes, Vietnam is a member of the Madrid Agreement and Protocol. You can designate Vietnam in an international application through the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
When to Hire a Lawyer
Navigating the Intellectual Property Office of Vietnam requires specialized expertise, particularly for tech firms dealing with complex patents or software copyright. You should hire an intellectual property lawyer if:
- You are entering a Joint Venture or licensing agreement with a Vietnamese entity.
- You discover a "squatter" has registered your brand or domain name.
- You need to conduct a professional "Freedom to Operate" (FTO) search.
- You are facing a "cease and desist" letter or need to issue one to a local infringer.
Next Steps
- Audit your Portfolio: Identify which software modules, brands, and hardware designs are currently unprotected in Vietnam.
- Contact an IP Agent: Foreign firms cannot file directly; you must appoint a licensed Vietnamese IP representative.
- Secure Evidence of Use: Keep records of your brand's global use and reputation, as these are vital if you need to challenge a "bad faith" filing.
- Update Contracts: Review your NDAs and employment agreements to ensure they comply with the 2022/2023 Amended IP Law standards for 2026.



